Interdependence
- In order to survive and reproduce (have offspring), organisms need certain resources from their surroundings (from the ecosystem they are living in)
- This means that members of a species will often interact with members of its own species or other species
- Some examples of these interactions include:
- Predators (carnivores) eating prey
- Herbivores eating plants
- Plant species being pollinated by bees
- Within a community, each species depends on other species for food, shelter, pollination, seed dispersal etc.
- This means that a change in the population of one species can have significant knock-on effects for other species in the same community
- If one species is removed it can also affect the whole community
- This is called interdependence
- A stable community is one where all the species and environmental factors are in balance so that population sizes remain fairly constant
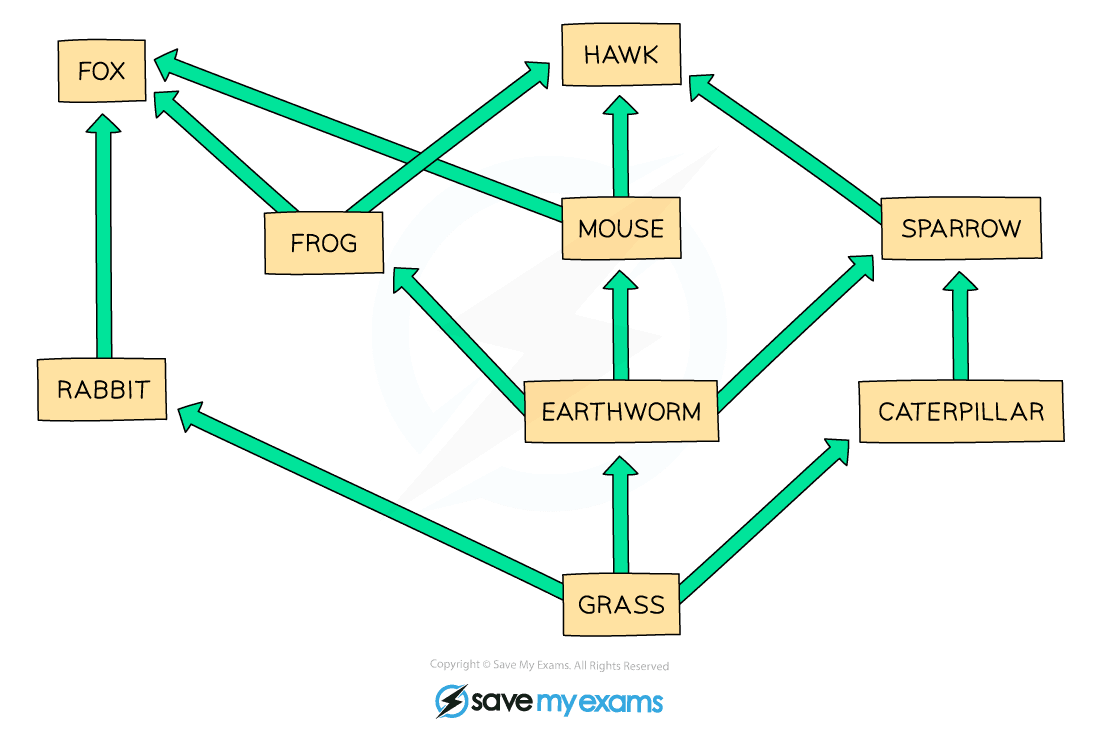
A food web shows the interdependence of organisms
- For example, in the food web above, if the population of earthworms decreased:
- The population of grass plants would increase as there are now fewer species feeding off them
- The populations of frogs and mice would decrease significantly as earthworms are their only food source
- The population of sparrows would decrease slightly as they eat earthworms but also have another food source to rely on (caterpillars)
Exam Tip
Questions about interdependence in food webs are common and simple to gain marks on if you answer them fully and correctly.
Do not say an animal or plant would ‘die out’ as this is unlikely to happen – stick to using the words decrease or increase (in the population of a species). If in doubt, always give your reason for the increase or decrease in population.