Antibiotics
- When treating a disease there are two types of medication that an individual can take:
- Medicines that treat the cause of the disease – e.g. antibiotics
- Medicines which treat the symptoms of the disease – e.g. painkillers
- Antibiotics, such as penicillin, are medicines that help to cure bacterial disease by killing infective bacteria inside the body
- The use of antibiotics has greatly reduced the deaths from infections in the last century
- Only certain antibiotics will work on certain diseases, however, so a doctor will prescribe different antibiotics depending on the type of infection
- It is important that specific bacteria should be treated by specific antibiotics that are known to work against them
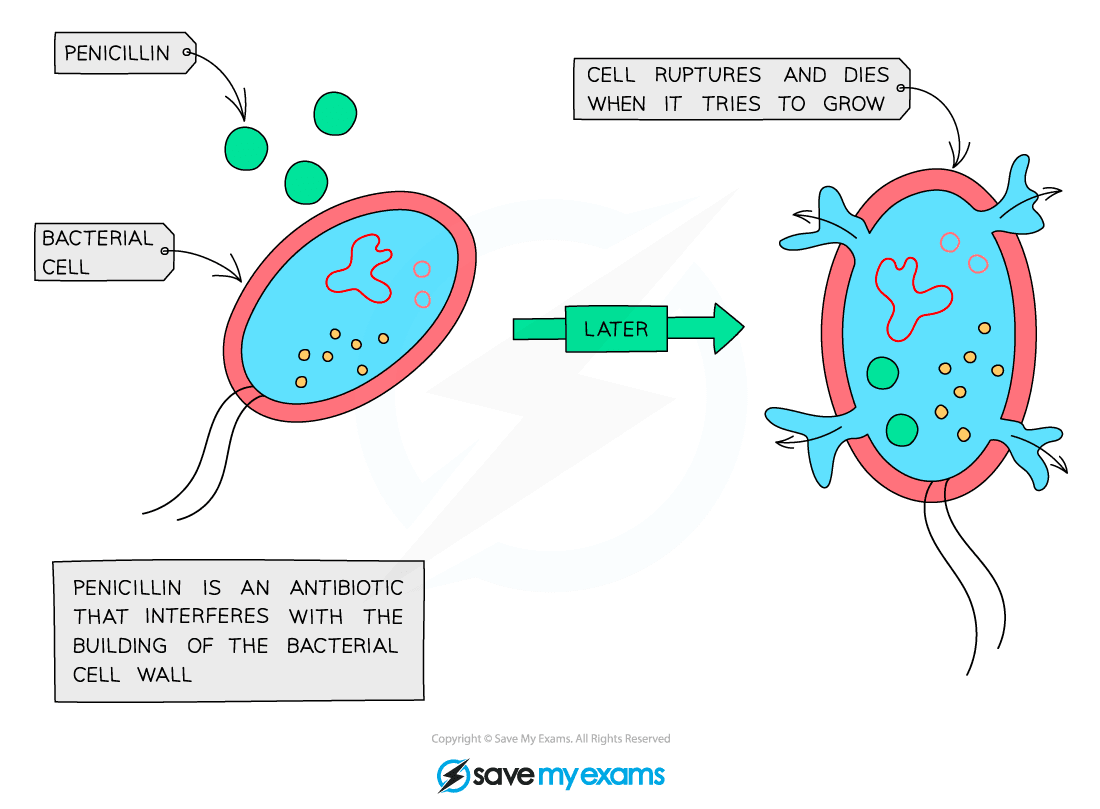
- Antibiotics work by inhibiting the processes in the bacterial cells, such as the production of the cell wall
- They affect processes usually only in bacteria so are not harmful to host cells
Penicillin was the first antibiotic to be discovered and is widely used, although resistance is a problem
- Antibiotics will not work against viruses, as viruses reproduce inside cells. It is difficult to develop drugs that kill viruses without also damaging the host’s tissues