Importance of Homeostasis
- Homeostasis is defined as the maintenance of a constant internal environment
- This means that internal conditions within your body (such as temperature, blood pressure, water concentration, glucose concentration etc) need to be kept within set limits in order to ensure that reactions in body cells can function and therefore the organism as a whole can live
- When one of these conditions deviates far away from the normal and is not brought back within set limits the body will not function properly and the eventual consequence without medical intervention will be death
- This is why diabetics need to control glucose intake (as their body cannot regulate it for them), why an extremely high and prolonged fever will kill you or why drinking too little or too much water can damage cells throughout the body – especially the kidneys and brain – and lead to death within days
Negative feedback and homeostasis
- Most homeostatic mechanisms in the body are controlled by a process known as negative feedback
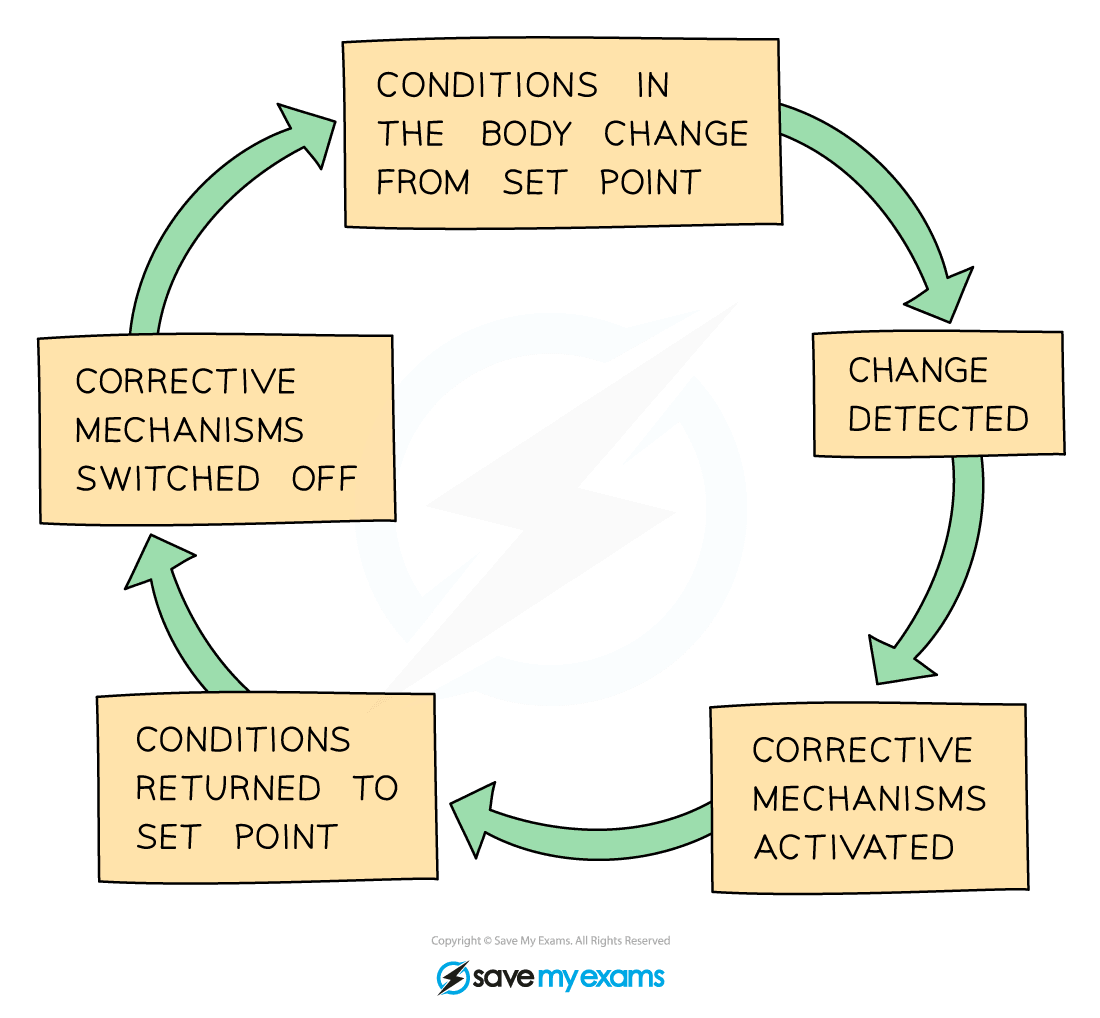
- Negative feedback occurs when conditions change from the ideal or set point and returns conditions to this set point
- It works in the following way:
- if the level of something rises, control systems are switched on to reduce it again
- if the level of something falls, control systems are switched on to raise it again
- Negative feedback mechanisms are usually a continuous cycle of bringing levels down and then bringing them back up so that overall, they stay within a narrow range of what is considered ‘normal’

Negative feedback mechanisms