Manufacture of Aluminium, Chlorine, Hydrogen & Sodium Hydroxide
Extraction of aluminium
- The Earth’s Crust contains metals and metal compounds such as Gold, Iron Oxide and Aluminium Oxide, but when found in the Earth, these are often mixed with other substances
- To be useful, the metals have to be extracted from their ore through processes such as electrolysis, using a blast furnace or by reacting with more reactive material
- Metals which lie above carbon have to be extracted by electrolysis as they are too reactive
Reactivity series & extraction of metals
Extraction of aluminium by electrolysis
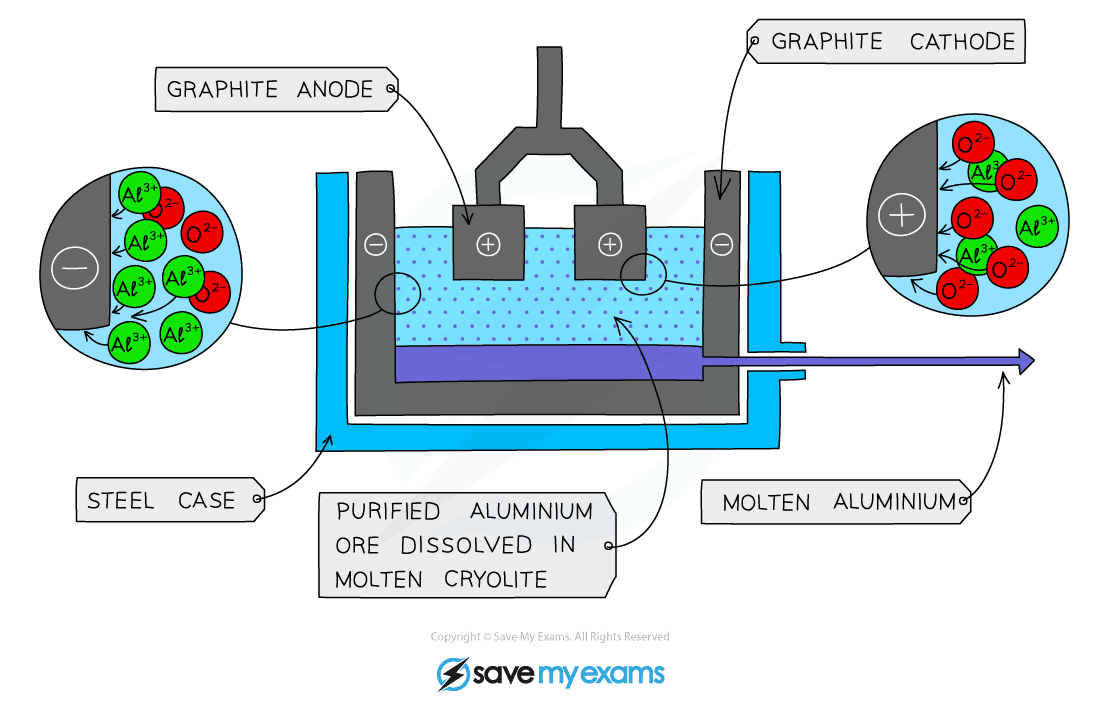
Diagram showing the extraction of aluminium by electrolysis
Raw Materials: Aluminium Ore (Bauxite)
Explanation:
- The Bauxite is first purified to produce Aluminium Oxide Al2O3
- Aluminium Oxide has a very high melting point so it is first dissolved in molten cryolite producing an electrolyte with a lower melting point, as well as a better conductor of electricity than molten aluminium oxide. This also reduces expense considerably
- The electrolyte is a solution of aluminium oxide in molten cryolite at a temperature of about 1000 °C. The molten aluminium is siphoned off from time to time and fresh aluminium oxide is added to the cell. The cell operates at 5-6 volts and with a current of 100,000 amps. The heat generated by the huge current keeps the electrolyte molten
- A lot of electricity is required for this process of extraction, this is a major expense
Reaction at the Negative Electrode:
The Aluminium melts and collects at the bottom of the cell and is then tapped off:
Al3+ + 3e- → Al
Reaction at the Positive Electrode:
2O2- – 4e– → O2
Some of the Oxygen Produced at the positive electrode then reacts with the Graphite (Carbon) electrode to produce Carbon Dioxide Gas:
C (s) + O2 (g) → CO2 (g)
*This causes the carbon anodes to burn away, so they must be replaced regularly.
Manufacture of chlorine, hydrogen and sodium hydroxide
- Brine is a concentrated solution of aqueous sodium chloride
- When electrolysed it produces chlorine, hydrogen and sodium hydroxide
- The electrolyte is concentrated sodium chloride which contains the following ions: H+, Cl– and OH–
- The H+ ions are discharged at the cathode as hydrogen gas
- The Cl– ions are discharged at the anode as chlorine gas
- The Na+ and OH– ions remain behind and form the NaOH solution
Diagram showing the products of the electrolysis of brine