Electron Arrangement in Complex Covalent Molecules
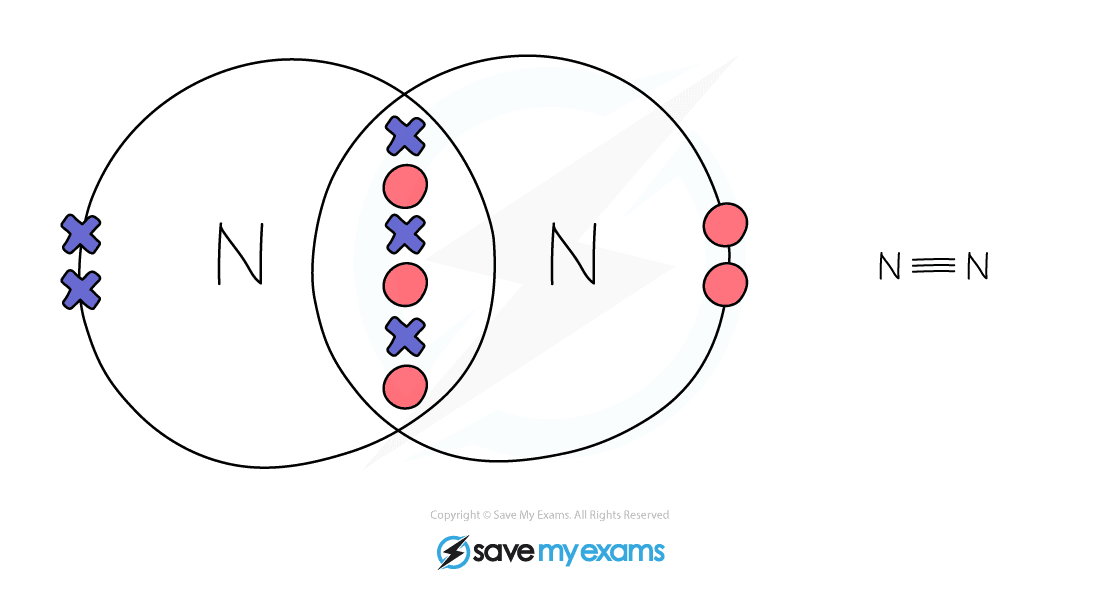
Nitrogen:
C2H4 (ethene):
CH3OH (methanol):
CO2:
Extended Only
Melting & Boiling Points of Ionic & Covalent Compounds
- Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points
- This is because the oppositely charged ions in the lattice structure are attracted to each other by strong electrostatic forces which hold them firmly in place
- Large amounts of energy are needed to overcome these forces so the m.p. and b.p. are high
- Simple covalent substances, such as carbon dioxide and methane, have very strong covalent bonds between the atoms in each molecule, but much weaker intermolecular forces between individual molecules
- When one of these substances melts or boils, it is these weak intermolecular forces that break, not the strong covalent bonds
- Less energy is needed to break the molecules apart, so they have lower m.p. and b.p. than ionic compounds