Trophic Levels & Food Chains
Trophic levels
- Trophic levels are used to describe the feeding relationships between organisms
- The Sun is the source of energy for nearly all life on Earth
- Energy flows from the Sun to the first trophic level (producers) in the form of light
- Producers then convert light energy into chemical energy and it flows in this form from one consumer to the next
- For example, plants (one type of producers) convert a small percentage of the light energy that falls on them into glucose, some of which is used immediately in respiration and some of which is stored as biomass
- When a primary consumer (e.g. a herbivore such as a rabbit) feeds on a plant, the chemical energy stored in the plant’s biomass is passed on to the primary consumer
- Eventually, all energy is transferred to the environment – energy is passed on from one level to the next with some being used and lost at each stage
- Energy is lost to the environment when heat energy is transferred from organisms to their surroundings
Trophic Levels Table
- Animals (known as consumers) can be at different trophic levels within the same food web as they may eat both primary, secondary and/or tertiary consumers
Food chains
- A simple way to illustrate the feeding interactions between the organisms in a community is with a food chain
- A food chain shows the transfer of energy from one organism to the next
- The source of all energy in a food chain is light energy from the sun
- The arrows in a food chain show the transfer of energy from one trophic level of the food chain to the next
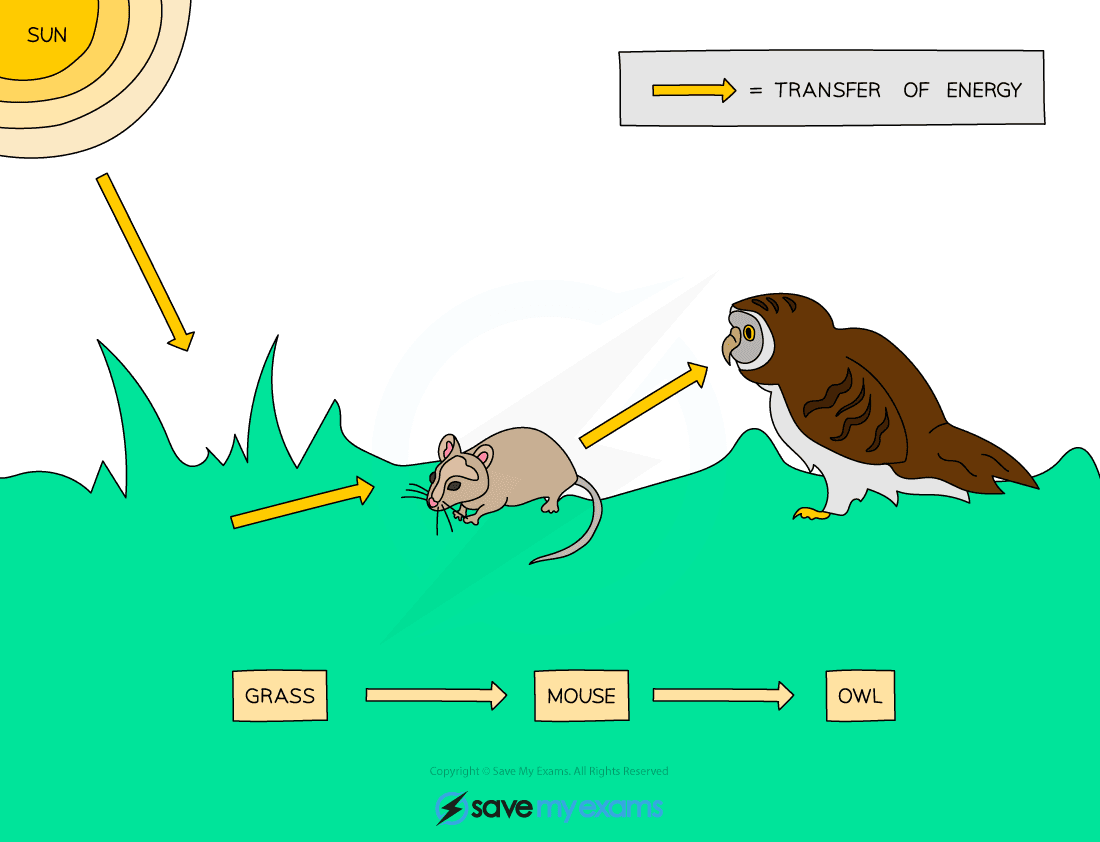
An example of a food chain (the sun is not included in food chains as it is not a living organism)
- You need to know the terms given to each step in a food chain (the sun is not included in food chains as it is not a living organism):
- Producer: food chains always begin with a producer
- Primary consumer: producers are eaten by primary consumers (herbivores/omnivores)
- Secondary consumer: primary consumers are eaten by secondary consumers (carnivores/omnivores)
- Tertiary consumer: secondary consumers are eaten by tertiary consumers (carnivores/omnivores)
Trophic levels for a simple food chain