Defects of the Eye
Short-sightedness
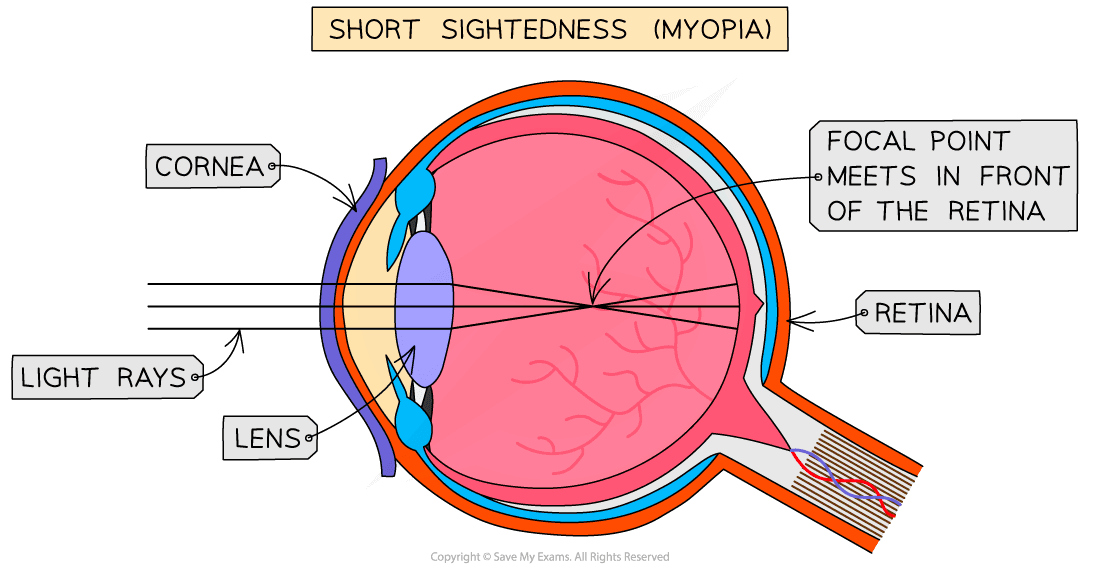
- Short-sightedness is also called myopia
- It happens when the lens is more curved than normal or the eyeball is too long which means the light is refracted too much and so the focal point falls in front of the retina (rather than on the retina)
- This means that distant objects appear blurry
Treatment of short-sightedness
- Short-sightedness can be corrected using contact lenses or glasses with a concave lens


Short-sightedness is caused when the lens is fatter than normal and so can be corrected using a concave lens
Long-sightedness
- Long-sightedness is also called hyperopia
- It happens when the lens is less curved than normal or the eyeball is too short which means the light is not refracted enough and so the focal point falls behind the retina (rather than on the retina)
- This means that close objects appear blurry
Treatment of long-sightedness
- Long-sightedness can be corrected using contact lenses or glasses with a convex lens


Long-sightedness is caused when the lens is thinner than normal and so can be corrected using a convex lens
Colour blindness
- People who suffer from colour blindness cannot distinguish between certain colours and in rare cases, cannot see colours at all
- This happens because the cones in the retina do not work properly or are absent
- It is a genetically inherited condition but can also develop over time
- There are several different types of colour blindness
Treatment of colour-blindness
- There is currently no cure for colour blindness (as the cone cells cannot be replaced) so most sufferers learn to live with the condition
Cataracts
- Cataracts is a condition in which a build up of protein causes clouding of the lens
- A cloudy lens means that the light is dispersed throughout the eye or absorbed by the lens, rather than being sharply focussed to one particular point
- This often leads to blurred vision
- Eventually, if left untreated, cataracts can lead to blindness
Treatment of cataracts
- Cataracts can be corrected by replacing the cloudy lens with an artificial one

Cataracts cause the lens to become cloudy which causes the light to be dispersed or absorbed